Understanding the USA's Climate: Zone Map, Weather Specifics, and Travel Tips
From deserts to tropics, snowy peaks to ocean shores, the USA boasts diverse landscapes. We detail the country's climate system, seasonal variations, and recommend ideal destinations for winter, spring, summer, and fall.
The USA is a vast country where the climate can drastically change from one state to another. While residents of Alaska bundle up in warm jackets, the sun shines in Florida, and California experiences its rainy season. This diversity makes the USA an ideal travel destination at any time of year, but it's important to consider the climatic features to ensure a comfortable trip.
In this article, we will break down the main climate zones of the country, discuss extreme weather events, and provide recommendations on where and when it's best to travel.
Climate Zones of the USA
The USA occupies a huge territory, which is why the climate varies significantly across different parts of the country. The north experiences harsh winters, the south has mild weather year-round, and the West Coast is characterized by warm, dry summers and rainy winters. Overall, several distinct climate zones are identified in the country.
Arctic and Subarctic Climate (Alaska)
Alaska is the only region in the USA where an arctic and subarctic climate prevails. In the northern part of the state, temperatures remain below freezing for most of the year, and winter lasts for six to eight months. In some areas, snow doesn't even melt in the summer. Southern Alaska has a milder climate, but winters are still cold, and precipitation falls as snow.
Continental Climate (Central States)
The central part of the USA encompasses the Great Plains and the Midwest. Summers here are hot, and winters can bring severe frosts. The weather changes abruptly due to the influence of air masses from the north and south. Spring and summer in this region often see tornadoes, especially in the so-called "Tornado Alley," which runs through Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, and Nebraska.
Mediterranean Climate (California)
California is known for its mild winters and warm, dry summers. This climate is typical of the US West Coast, particularly in the areas from San Francisco to Los Angeles. Precipitation mainly occurs in winter, while summers are consistently clear and sunny.
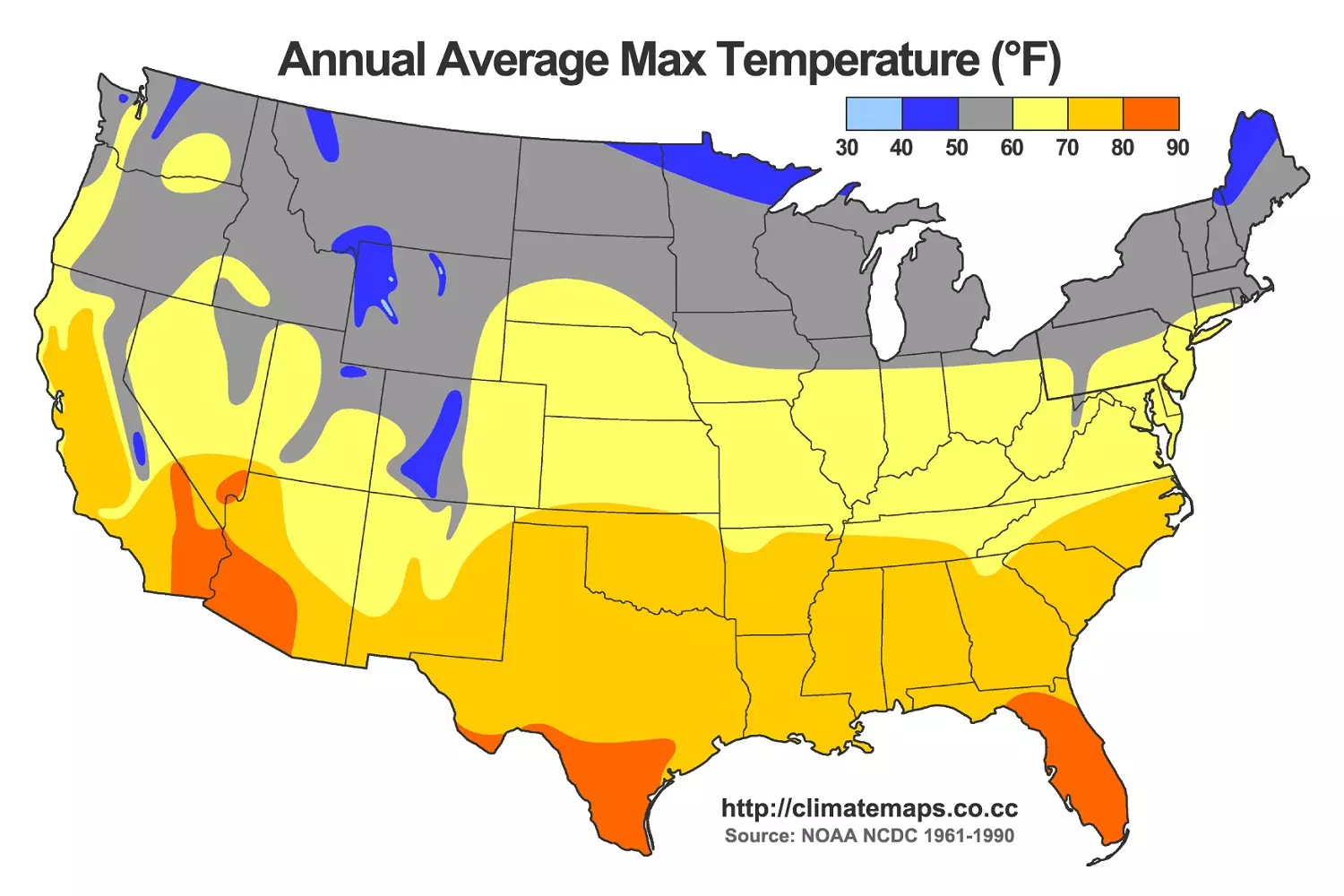
Subtropical Climate (Southern USA)
The southern states, such as Texas, Louisiana, Georgia, and North Carolina, are located in the subtropical climate zone. Summers here are hot and humid, with frequent rainfall. In winter, temperatures rarely drop below freezing, and snow is a rarity. Due to the high humidity, the air can feel heavy, especially in midsummer.
Tropical Climate (Florida and Hawaii)
Florida and Hawaii are situated in the tropical climate zone. Summers are hot and humid, and winters are warm and mild. Precipitation occurs year-round, but hurricanes are possible from June to November. In Hawaii, the climate is even more stable, with temperatures remaining fairly consistent throughout the year.
The variety of climate zones makes the USA an interesting destination for travel at any time of year. The key is to consider the weather conditions in your chosen region in advance.
Climate Features
The climate in the USA is diverse, ranging from harsh winters in the north to tropical heat in the south. The country's geographical location, its terrain, and the influence of the oceans create sharp contrasts in weather. In some regions, the weather changes gradually, while in others, it changes abruptly. Some states experience rain almost year-round, while others receive precipitation rarely.
Seasonal Changes in Temperature and Precipitation
Most regions of the country experience four distinct seasons, but their duration and characteristics depend on the geographical location.
- In the northern states, winters are cold with heavy snowfall. Summers remain temperate.
- In the central regions, summers can be hot, and winters severe. Temperature fluctuations can be abrupt.
- In the south and along the coasts, winters are mild, and summers are long and hot.
- In the arid regions of the West, the difference between daytime and nighttime temperatures can reach 20 degrees Celsius (68 degrees Fahrenheit).
The amount of precipitation also varies significantly. The West Coast and the Northeast receive a lot of rain, while the desert regions of the Southwest receive almost no precipitation.
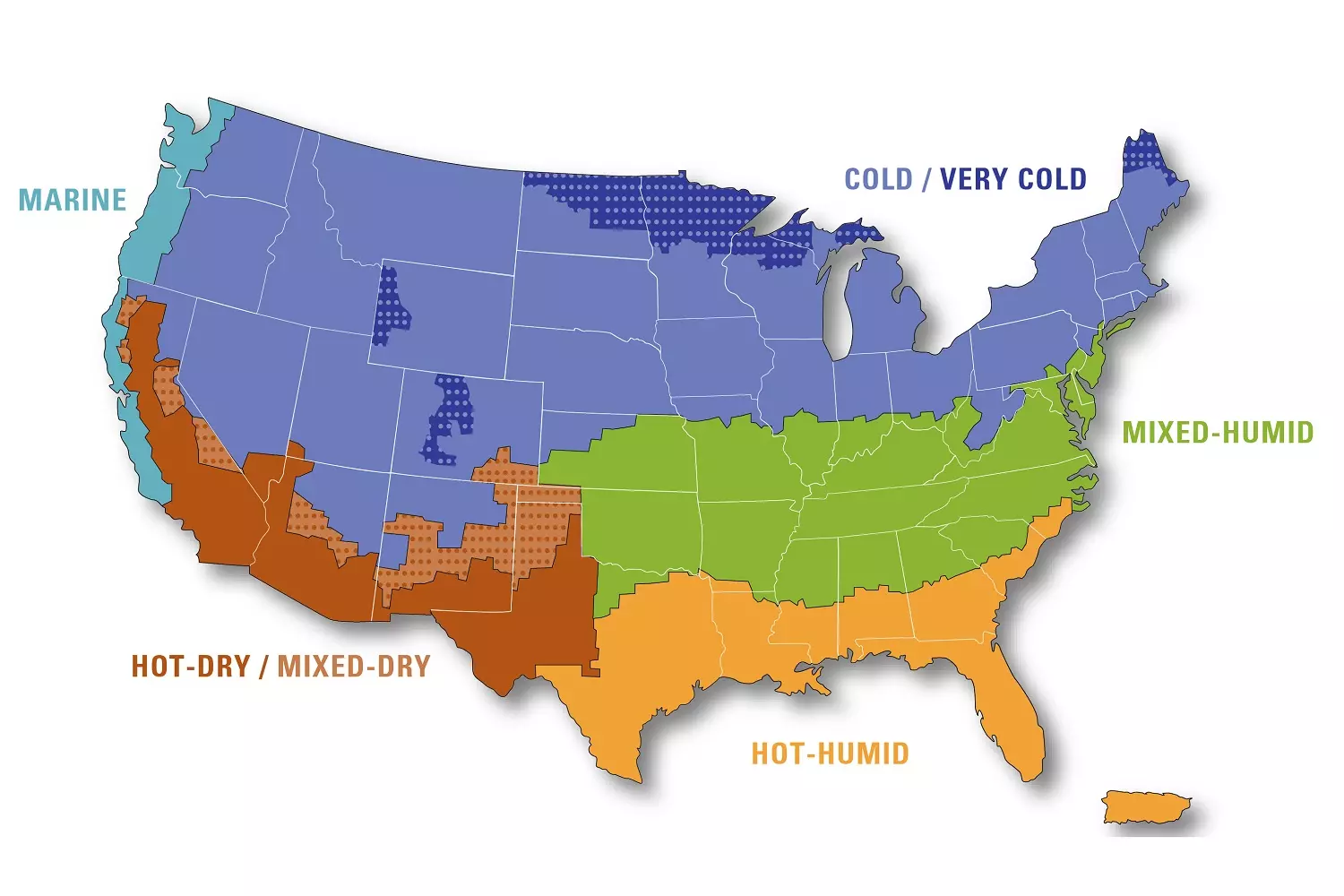
Influence of Oceans and Mountain Ranges
The Atlantic and Pacific Oceans influence the weather in coastal areas. The ocean moderates the climate: the West Coast of California has warm winters, and the East Coast of New York experiences less severe snowfalls than might be expected at the same temperatures inland.
Mountain ranges also play an important role. For example, the Rocky Mountains block moist air masses from the Pacific Ocean, so the western slopes receive a lot of precipitation, while the eastern slopes remain arid. The Appalachian Mountains in the east partially protect the coastal states from cold air masses from the north.
Extreme Weather Events
The USA is one of the countries with the most complex and dangerous weather conditions. In some regions, extreme weather occurs regularly.
- Tornadoes — most often occur in the central states, especially in the so-called "Tornado Alley." They can destroy homes, uproot trees, and overturn cars.
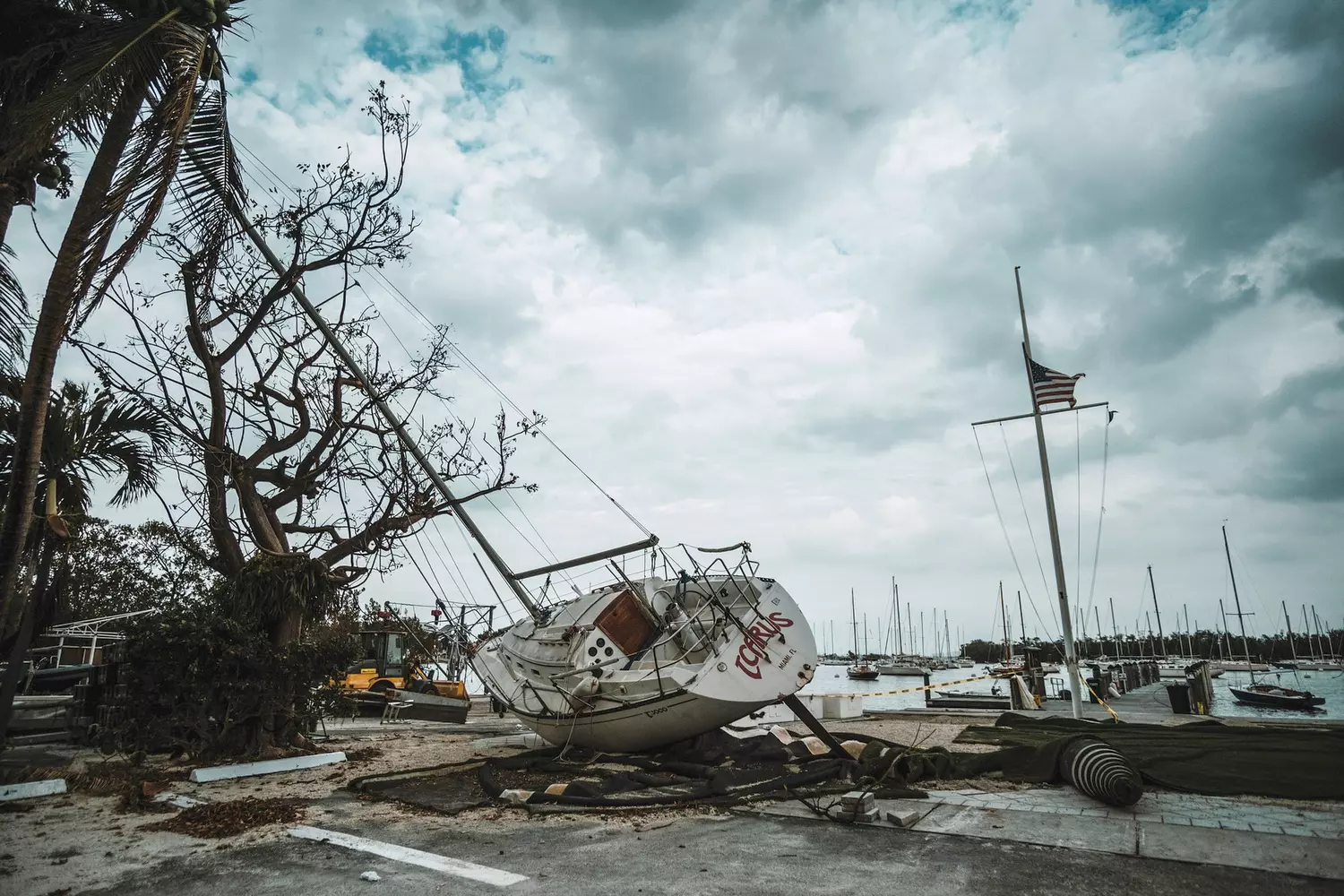
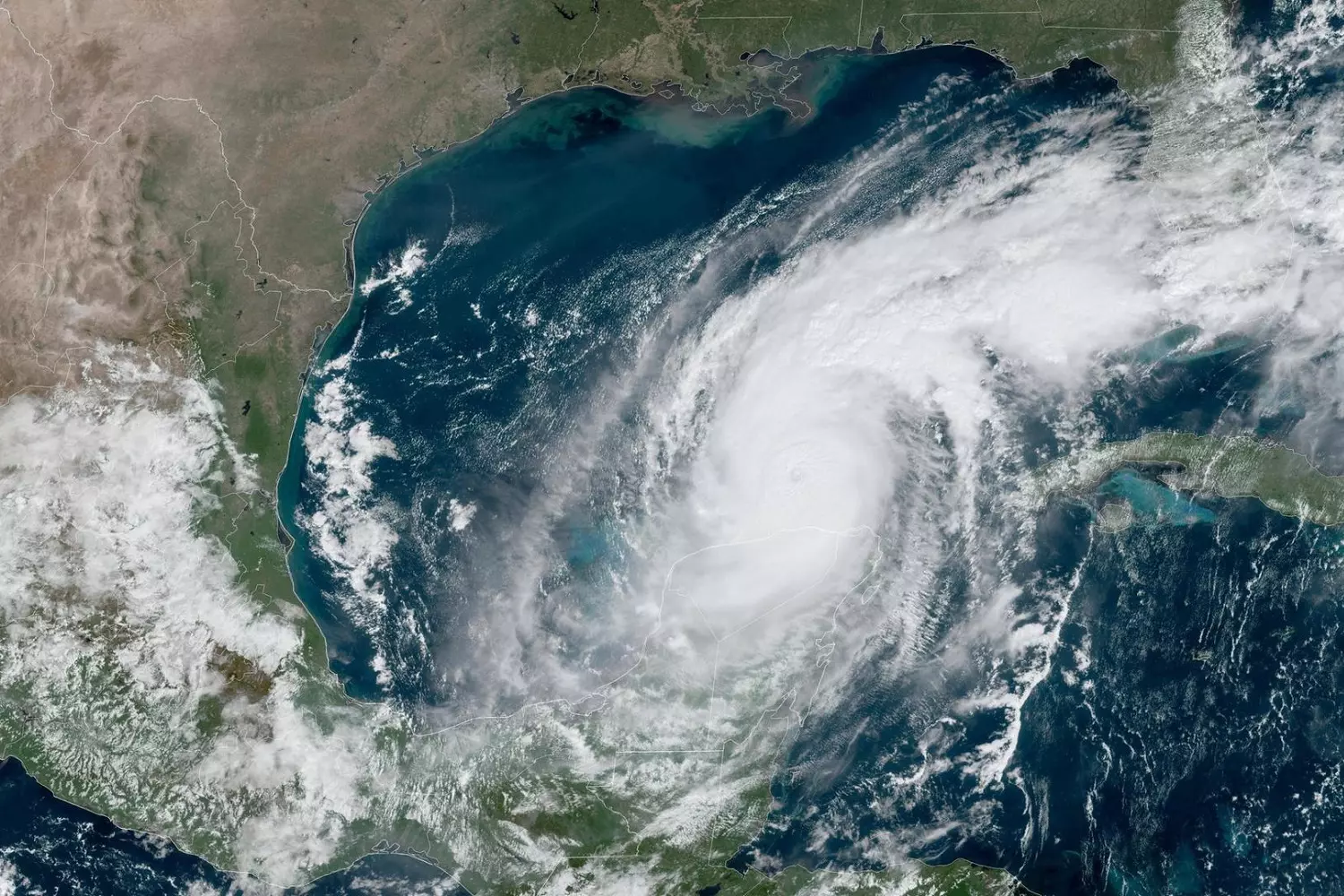
- Hurricanes — tropical storms that most often affect the East Coast, Florida, and the Gulf Coast. The most dangerous period is from June to November.
- Droughts — particularly characteristic of the southwestern states, such as Arizona and Nevada. Long periods without rain lead to fires.
- Heavy Snowfalls — occur in the north of the country, especially in the Great Lakes region and New England. Sometimes snowfalls paralyze cities for several days.
The climate of the USA is not only diverse but also prone to sudden changes. It is important to consider seasonal features when planning a trip to avoid unpleasant weather surprises.

Interesting Facts About the US Climate
The climate of the USA is diverse and full of unexpected contrasts. One part of the country might be experiencing heat, while another is simultaneously seeing snowfall. Weather records, unusual natural phenomena, and the influence of geography make the US climate truly unique.
The Hottest Place in the USA
Death Valley in California is considered the hottest place not only in the USA but also on the entire planet. A record temperature of +56.7 °C (134 °F) was recorded here. In summer, the air heats up to +50 °C (122 °F), and the sand and rocks become so hot they can burn skin.
The Coldest Place in the USA
The record low temperature was recorded in Alaska. In 1971, in the settlement of Prospect Creek, the thermometer dropped to –62.2 °C (–80 °F). Winters in Alaska are harsh, but even in January, temperatures in the southern part of the state can rise above freezing.
Where the Most Precipitation Falls
The city of Hilo in Hawaii is considered the rainiest in the USA. It receives an average of about 3300 mm (130 inches) of precipitation per year. It rains almost daily, especially during the winter season. Another record holder is Mount Waiʻaleʻale on the island of Kauai. It is one of the wettest places on the planet, where over 11,000 mm (433 inches) of precipitation can fall in a year.
Where the Snowiest Weather Occurs
The city of Syracuse in New York State is called the "Snow Capital" of the USA. The average annual snowfall here reaches 300 cm (118 inches). Even more snow falls in the Mount Baker area in Washington State. In 1998–1999, a record snowfall of almost 29 meters (95 feet) was recorded here during the winter.

States with the Most Variable Weather
In Montana, the temperature can change dramatically. In 1972, in the town of Loma, it rose from –48 °C (–54 °F) to +9 °C (48 °F) in just 24 hours. This is one of the most rapid temperature jumps in history. Another record holder is South Dakota, where the temperature dropped from +7 °C (45 °F) to –20 °C (–4 °F) in a single day.
Tornado Alley — A Zone of Increased Danger
The central part of the USA, especially Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, and Nebraska, is known for its high risk of tornadoes. Powerful vortices form here, capable of destroying houses and lifting cars into the air. On average, about 1,200 tornadoes occur in the USA each year — more than in any other country in the world.
The Sunniest State
Arizona and Nevada lead in the number of sunny days. In the city of Yuma, Arizona, the sun shines for an average of 4,000 hours per year. This makes it one of the sunniest places on the planet.
Arid Regions
The southwestern USA is known for its deserts. In some areas of California and Nevada, it almost never rains. For example, Death Valley can go an entire year without any precipitation.
When the Longest Rain Began
The longest continuous rainfall was recorded in the state of Hawaii. In 1993, on the island of Kauai, it rained non-stop for 247 days.
Where the Strongest Hurricanes Rage
The state of Florida is more often hit by hurricanes than any other. Due to the warm waters of the Atlantic, powerful storms form during the summer and autumn seasons, sometimes reaching destructive force. One of the strongest hurricanes — Hurricane Katrina — practically destroyed New Orleans in 2005.
The climate of the USA is not just comfortable weather on the beaches of Florida or California, but also extreme natural phenomena that are astonishing in their scale.
The Most Destructive Hurricanes in the U.S. in the 21st Century
Climate in Florida
Florida is located in the southeastern United States and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico. Thanks to its geographical position, the state has a warm climate that attracts tourists year-round. However, the weather here isn't always perfect — summers can bring heavy rainfall, and hurricanes are possible in the autumn.
General Climate Features
Florida is one of the warmest states in the USA. The average annual temperature ranges from +20 to +26 °C (68 to 79 °F). Even in winter, the temperature rarely drops below +10 °C (50 °F), and in the south, it practically never does.
Key climate features:
- High humidity throughout the year.
- Warm winters.
- Hot and rainy summers.
- Possibility of hurricanes in the autumn.
Florida is situated in the tropical and subtropical climate zones. The south, including Miami and Key West, has a tropical climate, while the central and northern parts (Orlando, Tampa, Jacksonville) have a subtropical climate.
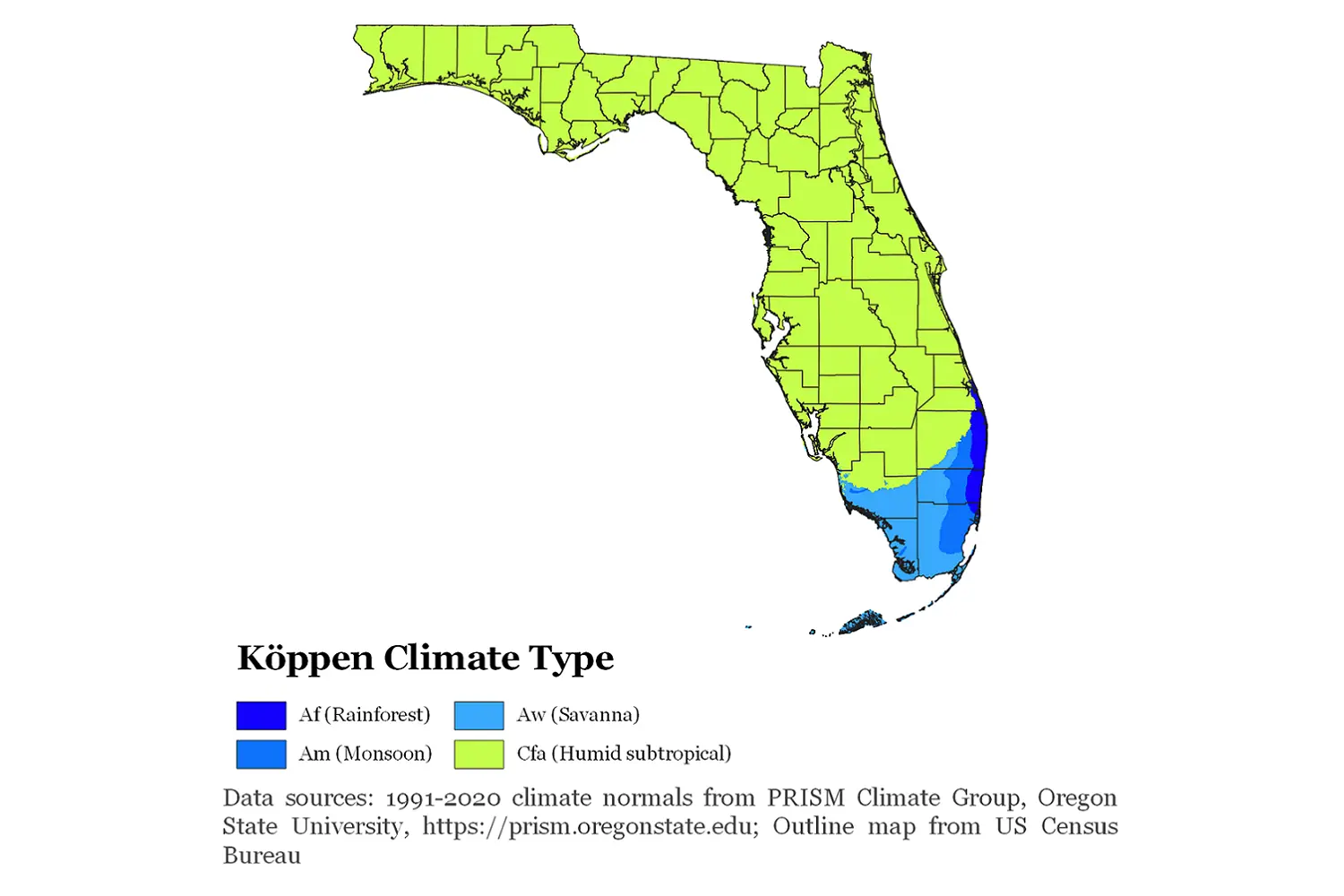
Seasons in Florida
Florida is divided not into the usual four seasons, but into two main seasons: dry and wet.
Dry Season (November — April)
This period is considered the best time to visit Florida.
- Temperature: +20…+25 °C (68…77 °F).
- Precipitation: rare rain.
- Humidity: lower than in summer.
- Wind: light breeze.
In winter, temperatures in the central and northern regions can drop to +10…+15 °C (50…59 °F), while the south remains comfortable at around +20 °C (68 °F). Snowfall is extremely rare here, but frosts occasionally occur in the northern part of the state.
Wet Season (May — October)
Summer in Florida is hot and humid, especially in July and August.
- Temperature: +30…+35 °C (86…95 °F).
- Precipitation: frequent and heavy showers.
- Humidity: high (up to 90%).
- Hurricanes are possible.
It rains almost every day, but the showers are short-lived – most often they are tropical downpours that last for 20–30 minutes. After they pass, the sun comes out again, but the air remains humid and muggy.
Hurricane Season
Florida is one of the most vulnerable states in the USA in terms of the number of hurricanes. The official season runs from June 1st to November 30th, but peak activity occurs in August and September.
Reasons for frequent hurricanes:
- Warm waters of the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico contribute to the formation of storms.
- Florida is located in the path of most hurricanes that form in the Caribbean Sea.
The strongest hurricanes in Florida's history:
- Hurricane Andrew (1992) — destroyed tens of thousands of homes in Miami.
- Hurricane Charley (2004) — caused damage to the southwest coast.
- Hurricane Irma (2017) — flooded coastal areas and left millions of people without electricity.
Despite the hurricanes, many tourists visit Florida even during the storm season, as modern technology allows for advance forecasting of their arrival.
When is the Best Time to Visit Florida?
- Winter and Spring (November — April) — the best time to travel. Comfortable temperatures, little rain, pleasant breeze.
- Summer (May — August) — beach vacation season, but high humidity and the possibility of rain can be uncomfortable.
- Autumn (September — November) — risk of hurricanes, but by the end of autumn, the weather becomes more stable.
Florida's climate makes this state a popular vacation destination at any time of year. The main thing is to consider the seasonal features to ensure a comfortable trip.

When and Where to Go
The USA is a vast country with a diverse climate, so it's important to consider the season and regional weather features for each trip. In some places, winter is mild and sunny, while in others it's cold and snowy. In summer, you can find both hot beaches and cool mountain resorts.
Winter (December — February)
In winter, it's best to go where it's warm or somewhere you can enjoy skiing.
Top Destinations:
- Florida — Miami, Key West, Orlando. Warm weather, beaches, entertainment at Disney and Universal parks.
- California — Los Angeles, San Diego. Comfortable temperatures and plenty of sunshine.
- Hawaii — ideal beach vacation even in January.
- Colorado, Utah, Vermont — ski resorts (Aspen, Park City, Stowe).
Winter is a good time to visit national parks in the Southwest, such as the Grand Canyon or Death Valley. It's not as hot there during this time of year.
Spring (March – May)
Spring is one of the best times to travel to the USA. The weather is comfortable, and there are fewer tourists than in summer.
Top Destinations:
- Washington D.C. — cherry blossoms in April.
- New York City — Central Park, city walks, museums.
- Texas — blooming meadows, pleasant temperatures.
- California Coast — Highway 1 road trip, San Francisco, Los Angeles.
In spring, you can visit national parks such as Yosemite, Yellowstone, and Sequoia. It's too hot there in summer, and nature blooms in spring.
Summer (June — August)
Summer in the USA is hot, especially in the South and central states. It's best to choose places with a moderate climate or beach destinations during this time.
Top Destinations:
- Western National Parks — Grand Canyon, Yellowstone, Bryce Canyon.
- Pacific Northwest Coast — Seattle, Portland, Olympic National Park. It's not as hot here.
- Alaska — the best time for cruises and whale watching.
- California — Santa Monica, San Diego, Big Sur.
It can be too hot in New York City, Washington D.C., and Las Vegas in the summer. If you go, be prepared for heat and humidity.
Autumn (September — November)
Autumn is an excellent time to travel to most regions of the USA. The weather is mild, there are fewer tourists, and nature is especially beautiful.
Top Destinations:
- New England — fall foliage in Massachusetts, Vermont, and New Hampshire.
- California — wineries in Napa, coastal drives.
- Florida — warm, but not as humid, and fewer tourists.
- National Parks — Grand Canyon, Zion, Arches.
Autumn is a good time to visit cities: Chicago, Boston, Washington D.C., San Francisco. The heat has subsided, but it's still warm enough for walking.
The USA is a country with a huge selection of climate zones and natural landscapes. At any time of the year, you can find a place for a comfortable trip. If you want a beach vacation, it's best to choose winter and spring. Spring and autumn are ideal for exploring cities. Nature lovers should go to national parks in spring and autumn when it's not hot.
It's important to consider seasonal features: it's cold in the north in winter, hot in the south in summer, and hurricanes are possible in Florida in autumn. If you are planning a trip during the high season, it's best to book accommodation in advance.

































